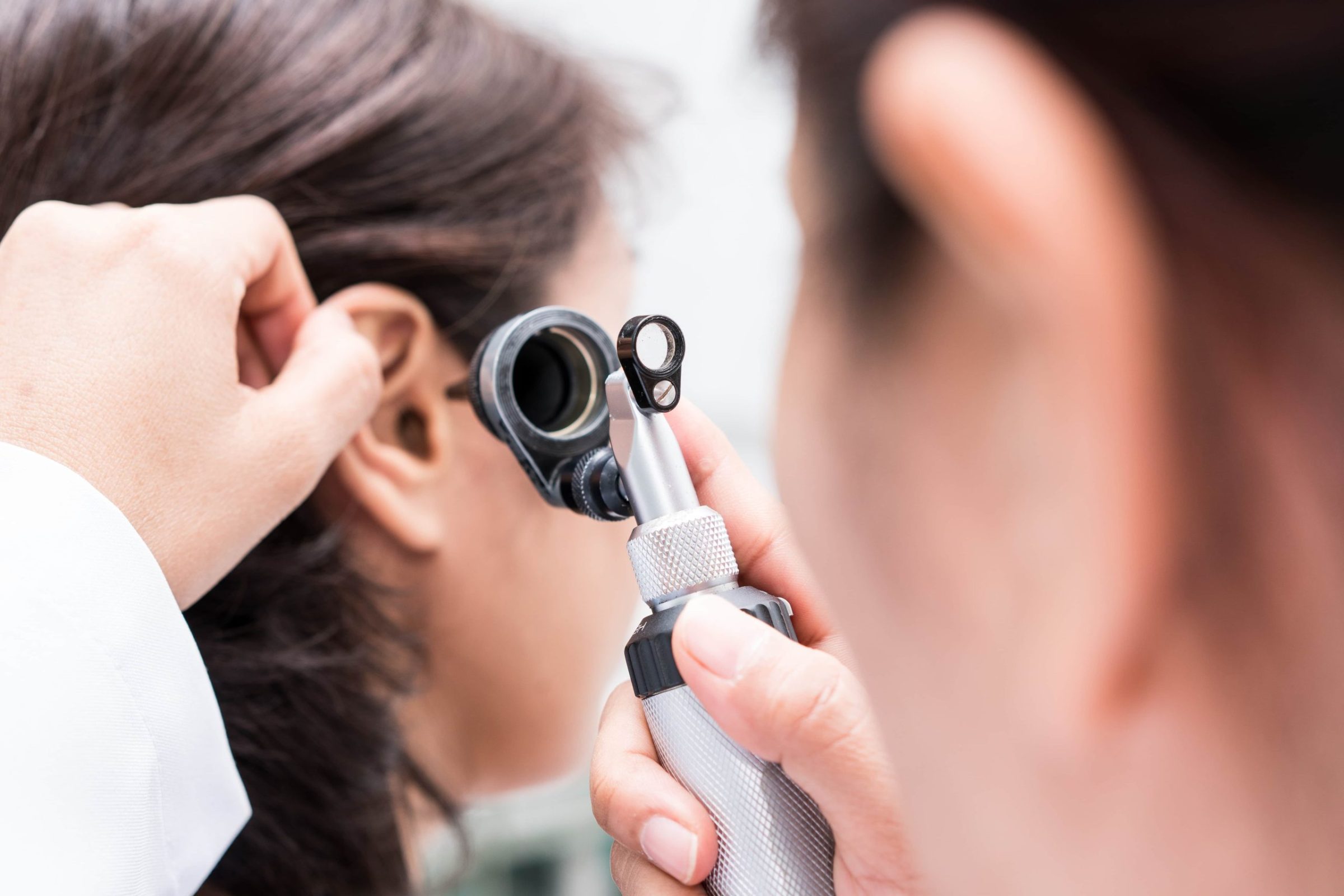
The hearing aid specialist plays an important role in the landscape of healthcare.
How to become a hearing aid specialist is challenging and rewarding. The specialist’s job encompasses a variety of diverse job duties with the overall goal of helping an individual hear to their fullest potential. The specialist is responsible for an initial hearing assessment, selection and fitting of appropriate hearing aids, along with ongoing care, maintenance, repair and adjustment of the hearing devices. It is a challenging yet rewarding occupation. Hearing aid specialists often work in conjunction with an audiologist or ear, nose and throat physician.
In California becoming a hearing aid specialist requires licensure as a Hearing Aid Dispenser. A licensure applicant must pass both a written and practical (hands-on) examination. Before the practical test can be taken, the applicant must first pass the written exam.
The written hearing aid dispenser’s exam assesses the following abilities of an applicant:
- Gathering relevant medical history of a patient.
- Inspection of the physical condition of a patient’s ear.
- Assessing the patient’s hearing acuity using standardized tests.
- Interpreting and communicating audiometric test results to a patient.
- Determining whether a patient may benefit from the use of hearing aids and providing options as necessary.
- Safely and accurately taking an ear impression.
- Determining whether a hearing instrument meets manufacturer and dispenser specifications.
- Validating the hearing aid fitting and instructing a client in the care and use of a hearing instrument.
- Identifying and resolving electronic and acoustic problems associated with common patient complaints associated with hearing aid use.
Once an applicant passes the written test he or she may take the practical exam. The practical exam is a rigorous, hands-on test that is performed under the watchful eye of a group of proctors. The proctors are experienced audiologists and hearing aid dispensers. Each applicant brings a test subject with them. The test is divided into different test stations where the proctors ensure that the applicant is able to perform the job duties in a safe and effective manner.
The content covered in the practical exam are:
- ear inspection
- audiometric assessment (hearing testing)
- ear canal impressions
- repairing hearing aids
- fitting hearing aids
- counseling after a hearing aid fit
After successfully passing both the written and practical test, state and federal background checks and fingerprint checks, they are eligible to be a licensed hearing aid dispenser. This is not the end of the journey on how to become a hearing aid specialist. Each year a hearing aid specialist is responsible for completing at least 12 hours of continuing education classes. These classes keep the specialist current with the latest scientific studies and technology as it relates to hearing healthcare.
Jonah Nishihira, B.A. is a hearing aid specialist at San Francisco Hearing Center located in the Presidio Heights neighborhood of San Francisco.